Wastewater Treatment Technology: BioFiltration,MBR, SBR, MBBR, AAO, AO, O, Physical-Chemical Treatment
Biofiltration
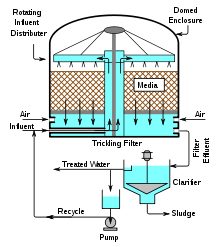
Technology feature: Use microorganism to biodegrade pollutants, microorganisms attached to filtering materials’ surfaces, when water passes through this filtering layer, pollutants are degraded.
Advantages:
– Low investment.
– Less energy required, comparing to activated sludge technologies.
Disadvantages:
– Subject to clogging.
– Small capacity.
– Susceptible to odor generation.
– Sensitive to temperature.
Application:
– Factories, hospitals.
– Small to medium capacity.
Membrane bioreactor (MBR)
Technology feature: Use microorganism to biodegrade pollutants, with physical membrane added.
Advantages:
– Compact.
– Effluent quality is always better than other conventional and biofilm technology, effluent is reusable.
Disadvantages:
– Subject to clogging.
– High MBR membrane investment and replacement cost.
– Difficult repair and replacement of MBR membrane because the membrane is only available imported.
Application:
– WWTP.
– Small to Large capacity.
– Plants with water reuse requirement.
Sequencing batch reactor (SBR)
Technology feature: Use microorganism to biodegrade pollutants, all reaction steps occur in one tank only and treatment occurs as batch.
Advantages:
– Automatic operation.
– Reduce equipments of sedimentation tank.
– Sludge recirculation is not needed.
Disadvantages:
– This technology requires open tank, so it does not fit with WWTP requires all underground tanks.
– This technology requires high degree of automation, so in case any incident happens, manual operation is difficult.
Application:
– Large scale projects.
– Average area WWTP.
Moving - bed bioreactor (MBBR)
Technology feature: Use microorganism to biodegrade pollutants, adding moving biofilm carrier to increase microorganism concentration retained in treatment tanks.
Advantages: Smaller occupied area and HRT than conventional AO/ A2O.
Disadvantages: Increase expense on biofilm carrier cost and maintenance cost.
Application:
– Waste water with biodegrable pollutants.
– Average-area WWTP.
Biological treatment: Anaerobic - Anoxic - Oxic (A2O)/ AO/ O
Technology features: Using microorganisms’ metabolism to biodegrade and transform biodegradable pollutants.
Treatment process: anaerobic (A) treats high-load BOD, COD, phosphorus, anoxic (A) treats Nitrogen and small amount of BOD, COD, Oxic (O) treats the remaining BOD and transform nitrogen.
Depends on waste water characteristics, 1, 2 or 3 treatment steps can be used.
Advantages:
– Little amount of sludge generated.
– Is a conventional and popular treatment methods, easy operation, can be programmed to automation.
– Effectively treat BOD, COD, Nitrogen, Phosphorus.
– Able to treat waste water of high organic load.
Disadvantages:
– Sensitive to temperature, pH, SS, heavy metals and other toxic components in influent waste water.
– Occupy average and above-average area.
Application:
AAO: waste water of food, husbandry and slaughtering, textile and dyeing industries… with high load of organic pollutants (high BOD, COD, phosphorus).
AO: waste water with high load of N, average BOD, COD (domestic waste water in general, industrial zone waste water, husbandry and slaughterhouse waste water…).
O: waste water contains average BOD, COD, little Nitrogen.
Treatment process: anaerobic (A) treats high-load BOD, COD, phosphorus, anoxic (A) treats Nitrogen and small amount of BOD, COD, Oxic (O) treats the remaining BOD and transform nitrogen.
Depends on waste water characteristics, 1, 2 or 3 treatment steps can be used.
Advantages:
– Little amount of sludge generated.
– Is a conventional and popular treatment methods, easy operation, can be programmed to automation.
– Effectively treat BOD, COD, Nitrogen, Phosphorus.
– Able to treat waste water of high organic load.
Disadvantages:
– Sensitive to temperature, pH, SS, heavy metals and other toxic components in influent waste water.
– Occupy average and above-average area.
Application:
AAO: waste water of food, husbandry and slaughtering, textile and dyeing industries… with high load of organic pollutants (high BOD, COD, phosphorus).
AO: waste water with high load of N, average BOD, COD (domestic waste water in general, industrial zone waste water, husbandry and slaughterhouse waste water…).
O: waste water contains average BOD, COD, little Nitrogen.
Physical - chemical treatment
Technology features: Using coagulant, flocculants, and if necessary, strong oxidizing agents to settle pollutants in waste water.
Advantages:
– Remove most of suspended solids (80-90% TSS), BOD5 (40-70%), COD (30-40%), part of nutrients (N and P), toxic heavy metals and microorganisms.
– Capable of treating small-sized colloidal pollutants.
Disadvantages:
– Large amount of sludge generated.
– Large amount of chemicals used.
Application:
– Before or after biological treatment.
– Industrial waste water with inorganic or inert pollutants that cannot be treated by biological treatment methods.
From http://www.ecobaent.vn/en/category/
Roy Sales Engineer
Membrane Solutions, LLC
(Cell)0086-15172323686
(Skype)roy.wong66

评论
发表评论